The present perfect tense is one of the most common English verb tenses, and it’s used in several different ways. This lesson will teach you everything you ever wanted to know about the present perfect – try the four quizzes with grammar exercises in each section!

Table of contents:
- What is the present perfect tense & when do we use it?
- How to form the present perfect: Positive, Negative, Questions
- What is the past participle?
- Present perfect with ever/never
- Present perfect with already, yet, recently, lately, just
- Present perfect with for and since
- Present perfect active voice and passive voice
- Present perfect simple vs. Present perfect continuous
What is the present perfect tense and when do we use it?
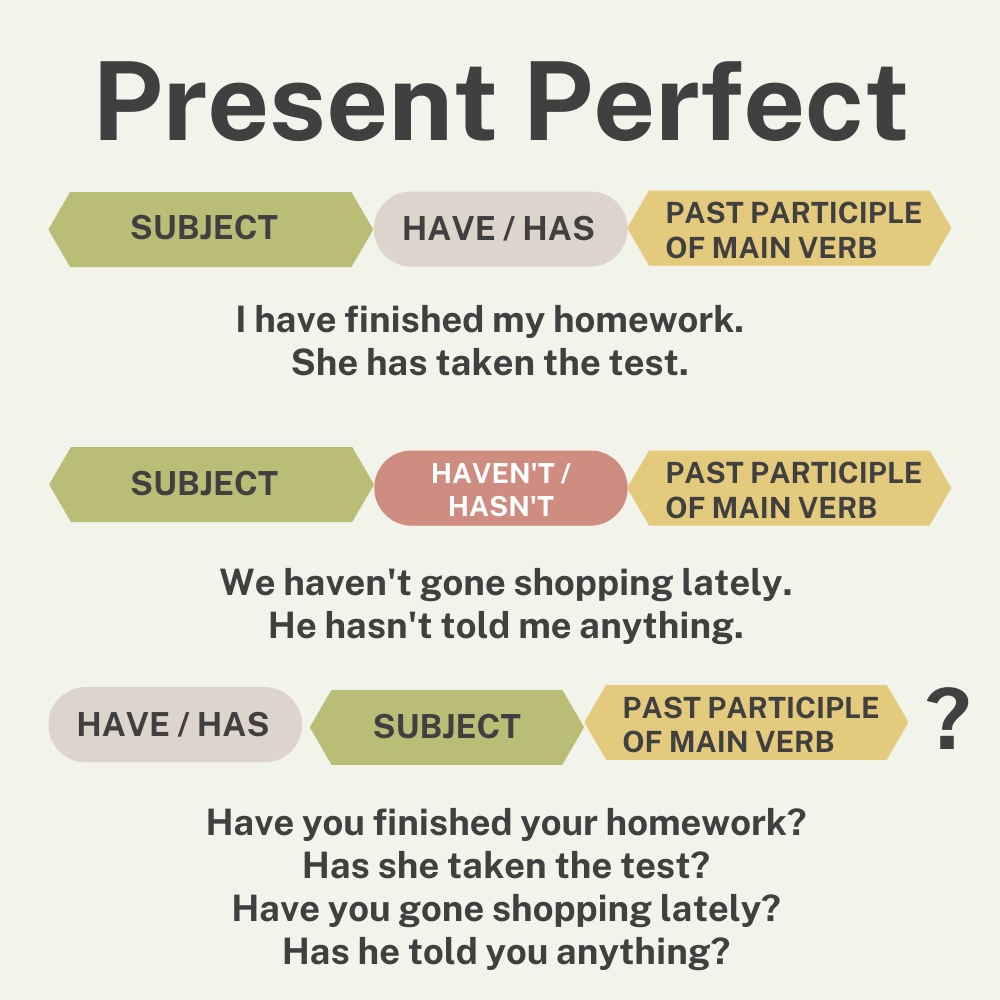
The present perfect is formed by subject + have/has + past participle of the main verb, for example:
- I have bought a car recently.
- I = subject, have = auxiliary verb, bought = past participle of the main verb “buy”
- She has visited the museum several times.
- She = subject, has = auxiliary verb, visited = past participle of the main verb “visit”
We use the present perfect for unfinished time (a period of time that continues to the present moment), differently from the simple past tense which describes finished time:
- Present Perfect: We have lived in New York since 2002.
(and we still live in New York) - Simple Past: We lived in New York from 2002-2006.
(and we do not still live in New York)
We also use the present perfect tense for unspecified time (when we don’t know or don’t say exactly when), differently from the simple past tense which describes specific time:
- Present Perfect: I‘ve seen that movie.
(I don’t say exactly when) - Simple Past: I saw that movie a year ago.
- Present Perfect: He has sold his house recently.
(it happened recently, but I don’t know exactly when) - Simple past: He sold his house last week.
More examples of present perfect vs. past simple

How to form the Present Perfect
Present Perfect Positive
| SUBJECT | HAVE / HAS | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| I / you / we / they | have | written |
| he / she / it | has | written |
Note: In spoken English, it’s common to use the contraction for the auxiliary verb have or has:
- I’ve written three books.
- We’ve already seen that movie
- Barbara’s forgotten her cell phone.
- He’s just woken up.
In this case, he’s, she’s, Barbara’s, etc. mean he has, she has, and Barbara has, not he is, she is, or Barbara is.
Present Perfect Negative
| SUBJECT | HAVEN’T / HASN’T | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| I / you / we / they | haven’t | seen |
| he / she / it | hasn’t | seen |
Example sentences:
- I haven’t seen John this week.
- Mary hasn’t come to class for the past two days.
Present Perfect Questions
| HAVE / HAS | SUBJECT | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| Have | I / you / we / they | finished? |
| Has | he / she / it | finished? |
Example sentences:
- Have you finished the project yet?
- Has George ever been to New York?
How to answer present perfect questions:
We can create a “short answer” using the auxiliary verb have/has, or their negative forms haven’t/hasn’t:
- Have you been to London?
Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t. - Has Alex met Miriam yet?
Yes, he has. / No, he hasn’t. - Have the results of the election been announced?
Yes, they have. / No, they haven’t.
Have had
In the present perfect, it’s possible to say “have had” and “has had” when “have” is BOTH the auxiliary verb (helping verb) AND the main verb in the sentence, for example:
- I‘ve had a lot of computer problems lately.
(I have had) - She’s had three children in the past five years.
(She has had) - We haven’t had time to visit our relatives.
- He hasn’t had a haircut for months.
Click here to learn more about HAVE HAD and HAD HAD
Click here to learn about the present perfect vs. past perfect
What is the past participle?
The past participle form of the verb describes a completed action or state.
For regular verbs, the past participle is the same as the past simple tense:
- I worked (simple past) all day yesterday.
- I’ve worked (past participle) here since August.
This is also the case for many irregular verbs:
- He sold (simple past) his car last week.
- He’s sold (past participle) 200 books so far.
However, some irregular verbs’ past participles are different from their simple past form:
- We wrote (simple past) an article for the newspaper.
- We’ve written (past participle) for many famous publications.
Many of these irregular past participles end in –n:
| Infinitive | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| be | was / were | been |
| break | broke | broken |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| do | did | done |
| drive | drove | driven |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| know | knew | known |
| see | saw | seen |
| show | showed | shown |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| take | took | taken |
| wear | wore | worn |
| write | wrote | written |
Other irregular past participles have a change in the vowel:
| Infinitive | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| come | came | come |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| ring | rang | rung |
| run | ran | run |
| sing | sang | sung |
| swim | swam | swum |
Present Perfect Quiz
Question 1 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 2 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 3 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 4 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 5 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 6 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 7 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 8 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 9 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 10 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 11 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 12 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 13 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 14 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 15 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Present Perfect tense with unfinished time
Present Perfect with ever / never
The present perfect is used with ever and never to talk about actions done at any time in a person’s life, or at any time in history until now.
- Have you ever been to Japan?
- Has she ever seen Titanic?
- Have they ever ridden a motorcycle?
- Has Jason ever failed a test?
Use ever in questions only – NOT in statements.
- “I’ve ever been to Japan.”
- “I’ve been to Japan.”
Use never in statements – but only with have/has, not with haven’t/hasn’t:
- “My sister hasn’t never seen Titanic.”
- “My sister has never seen Titanic.”
- “My sister hasn’t seen Titanic.”
Present Perfect with already, yet, recently, lately, and just
The words already, yet, recently, lately, and just all refer to a recent and non-specific time period. (A specific time would be “yesterday” or “three hours ago” or last Friday,” and in these cases we would use the simple past).
Already and yet
Already can be used in positive statements and questions.
- “I’ve already read today’s newspaper.”
- “Have you already paid the electric bill?”
- “She’s finished the test already.”
Note: Already can go in between “have/has” and the past participle (as in the first two examples) or at the end of the sentence.
Yet can be used in negative statements and questions.
- “We haven’t cleaned the house yet.”
- “Has he told you the good news yet?”
- “Have they booked their tickets yet?”
Note: Yet usually goes at the end of the sentence or phrase.
Recently, lately, and just
Recently and lately can be used in positive statements, negative statements, or questions:
Recently
- “He’s recently lost some weight.”
- “I haven’t seen her recently.”
- “Have you spoken to Beth recently?”
Lately
- “I’ve gotten a lot of spam e-mails lately.”
- “Adam and Jessica haven’t been to church lately.”
- “Have you seen any good movies lately?”
Just (usually means very recent) is typically only used in positive statements and questions:
- “Don’t touch the walls – I’ve just painted them and they’re still wet.”
- “What book have you just finished reading?”
Spoken American English often uses the simple past with already, yet, and just:
- “Did you book the tickets yet?”
- “I already replied to the e-mail.”
- “We just got back from the gym.”
Quiz: Present Perfect with ever, never, already, recently, lately, and just
Question 1 |
A | ever |
B | never |
C | recently |
Question 2 |
A | ever |
B | lately |
C | never |
Question 3 |
A | ever |
B | already |
C | lately |
Question 4 |
A | never |
B | already |
C | recently |
Question 5 |
A | yet |
B | ever |
C | just |
Question 6 |
A | just |
B | yet |
C | lately |
Question 7 |
A | lately |
B | just |
C | never |
Present Perfect with for and since
The present perfect is also used with for and since to talk about actions that began in the past and continue to the present.
- “I’ve lived here since 2004.”
- “I’ve lived here for 8 years.”
Since is used with a point in time, and means “from that point in time until the present.” Use since with dates (2011, January, Tuesday, etc.), times (6:15, noon, this morning, etc.), and past events (I was a child, he graduated from college, etc).
Since is always used with the present perfect, and not the simple past:
- “I’ve gone to the beach every year since I was a child.”
(repeated action that continues until today) - “I went to the beach when I was a child.”
(finished action at a specific time in the past; I don’t go to the beach today)
For is used with a time period, and means “for that period of time until the present.” Use for with time periods of any length (five seconds, eight hours, two days, six weeks, nine months, ten years, a decade, centuries, etc.)
Be careful with for, because using the present perfect or the simple past can change the meaning:
- “We’ve lived in Berlin for 6 months.” (and we live in Berlin now)
- “We lived in Berlin for 6 months.” (and we don’t live in Berlin now)
Quiz: Present perfect with FOR and SINCE
Question 1 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 2 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 3 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 4 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 5 |
A | since |
B | for |
Question 6 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 7 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 8 |
A | since |
B | for |
Question 9 |
A | for |
B | since |
Question 10 |
A | for |
B | since |
Present Perfect Active Voice & Passive Voice
We can also form passive voice sentences with the present perfect tense! Here’s how to do it:
- Active voice: I have sent the packages.
- Passive voice: The packages have been sent.
- Active voice: He has fixed the car.
- Passive voice: The car has been fixed.
The passive voice of the present perfect tense needs two auxiliary verbs: have/has + been + main verb.
Note that whether we use “have” or “has” depends on the new subject of the passive sentence (the receiver of the action):
- Active voice: I have sent the letter.
- Passive voice: The letter has been sent.
- Active voice: He has fixed the wheels.
- Passive voice: The wheels have been fixed.
Present Perfect Simple vs. Present Perfect Continuous
How to form the Present Perfect Continuous:
Positive and Negative Statements:
| SUBJECT | AUXILIARY VERB | BEEN | -ING FORM |
| I | have | been | working here since 1992. |
| He | hasn’t | been | sleeping well lately. |
Questions:
| QUESTION WORD | AUXILIARY VERB | SUBJECT | BEEN | -ING FORM |
| How long | have | you | been | studying English? |
| How long | has | she | been | playing tennis? |
In some cases, the present perfect simple and the present perfect continuous are the same:
- “I’ve worked here since 1992.” = “I’ve been working here since 1992.”
However, we often use the present perfect continuous to emphasize the action, and the present perfect simple to emphasize the result:
- “I’ve been working on this report for three weeks.”
(emphasizes the action of working) - “I’ve finished the project.”
(emphasizes that the project is done) - “We’ve been cleaning the house all afternoon.”
(emphasizes the action of cleaning) - “We’ve cleaned the bathroom and the kitchen.”
(emphasizes the fact that the bathroom and kitchen are done)
Be careful: Remember that stative verbs (describing the status of something) are never used in the present perfect continuous:
- “I’ve been knowing my best friend since elementary school.”
- “I’ve known my best friend since elementary school.”
- “She’s been understanding everything in the advanced class so far.”
- “She’s understood everything in the advanced class so far.”
In spoken English, we often use the present perfect continuous to talk about ways you have spent your time recently:
“Hi, Joanna! What have you been up to lately?”
“I’ve been training for a karate competition.”
“Wow – good luck! And how is your son?”
“He’s good. He’s been studying a lot lately because finals are coming up next week.”
Quiz: Present Perfect Continuous / Present Perfect Simple
Question 1 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 2 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 3 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 4 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 5 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 6 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 7 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 8 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 9 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Question 10 |
A | Correct |
B | Incorrect |
Now you know all about the present perfect tense in English!
Click here to learn about more English verb tenses.
Make sure to put it into practice by writing your own example sentences with this verb tense.
What’s next for learning English grammar? Join my Advanced English Grammar Course to learn in detail about verb tenses, advanced sentence structure, nouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, and much more.
The lessons will help you not only understand English grammar rules, but also put grammar in use in your own English. You can even send in your written English for correction.












